Hearing losses
Reduced hearing
Hearing losses sneak up on us. It can be hard to notice when our ability to hear is reduced because we can compensate for it by turning up the radio volume for example.
- It is as if other people are mumbling.
- It is hard to hear conversation with background noise, such as in large groups.
- A person may often ask for things to be repeated.
- It becomes necessary to turn up the TV or radio volume.
Hearing can be lost as a result of single exposures to very loud noise, but it is often longer daily exposure that injures hearing – hearing wears with time.
Hearing losses develop quickest in the first year of exposure to the noise, typically while young. This hearing loss will appear as an additional decrease of the hearing caused by age.
Sound is transmitted through the ear to the inner hearing organ, called the inner ear. In the inner ear there are over 20,000 microscopic “hair cells” that convert the motion caused by the sound into nerve impulses which are then sent to the brain.
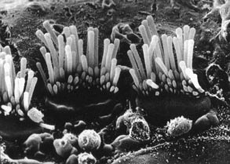
Foto: Berit Engström
Hair cells in a normal ear without hearing loss. These fine hairs are set in motion due to the incoming sound. The higher the level of the sound, the more the hairs move. Via the hair cells movement, sound waves are converted to nerve impulses, which are sent to the brain.
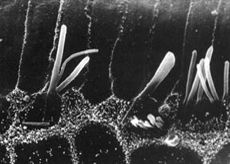
Foto: Berit Engström
Hair cells in an ear with a hearing loss. After a high noise exposure the hair cells become destroyed. These few remaining hairs are only slightly able to convert the sound signals into nerve impulses – a permanent hearing loss is inflicted.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is the howl, ring or whistle heard when there is no actual sound. Everyone can have a small amount of Tinnitus, but for some the experience of the sound becomes so strong that it becomes a serious disability. Among other causes, Tinnitus can be a result of high exposure to noise. Tinnitus can not actually be measured.
Tinnitus can be disabling
Accidents
Heavy noise reduces attention and makes it difficult to hear warning sounds and to communicate.
Noise increases the risk for accidents
